Introduction to Plastic Molding Technology
Plastic molding processing is an engineering technology involving various processes to transform plastic into products. This transformation often includes phenomena such as polymer rheology and changes in physical and chemical properties.
What is Compression Molding?
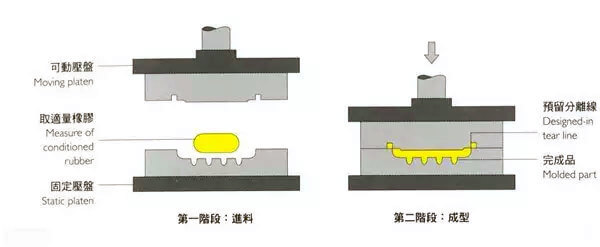
Compression molding, also known as press molding, is a primary method for forming thermosetting plastics and reinforced plastics. This process involves placing raw materials in heated molds under pressure, allowing the materials to flow and fill the cavity, and forming products through heat and pressure over time.
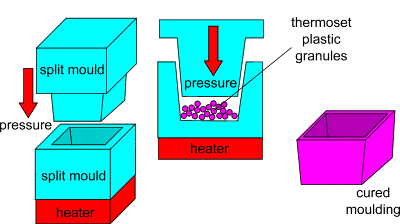
Characteristics and Performance of Thermosetting Plastic Compression Molding
Process Characteristics
- Mature technology with simple equipment and molds compared to injection molding.
- Intermittent molding with longer production cycles and lower efficiency.
- Produces high-quality products without internal stress or molecular orientation.
- Can mold large-area products but not complex shapes or thick items.
- Allows for hot demolding of products.
Performance Factors
Key performance factors include:
- Fluidity: The flowability impacts the molding process and product quality.
- Curing Rate: Influences the chemical reaction speed during molding.
- Shrinkage Rate: Affects dimensions and product integrity post-molding.
- Compression Ratio: Relates to volume change during molding.
- Moisture and Volatiles Content: Excessive content can affect product quality.
- Fineness and Uniformity: Particle size and distribution play a role in performance.
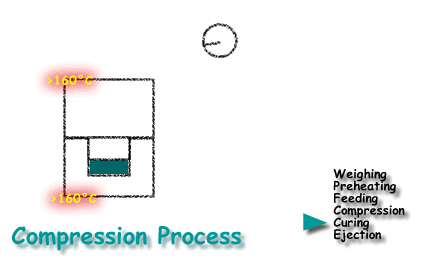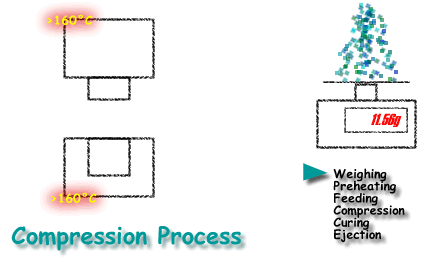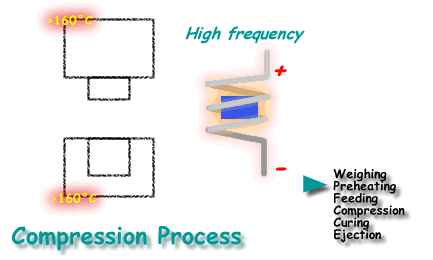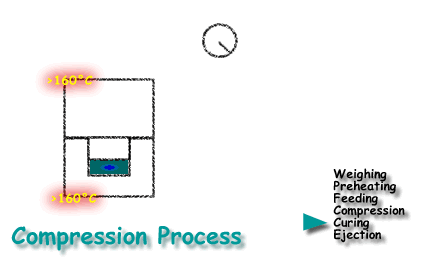
Equipment and Molds Used in Compression Molding
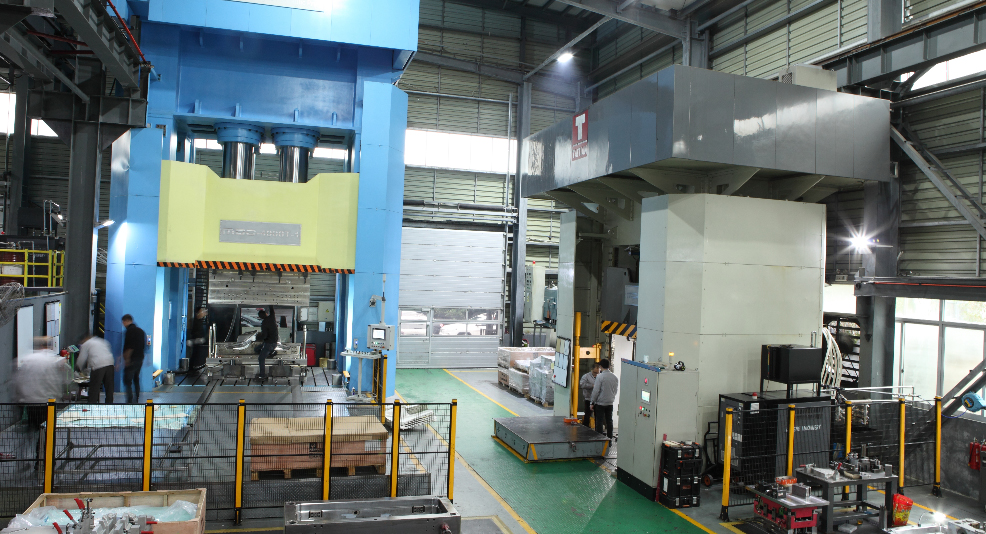
The main equipment used is the press machine, which applies heat and pressure to the plastic through molds. There are two main types of hydraulic presses:
- Top-pressing hydraulic machines.
- Bottom-pressing hydraulic machines.

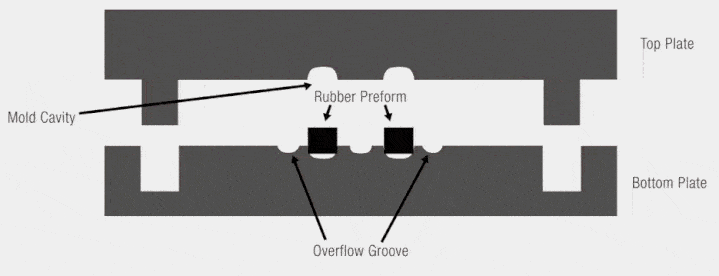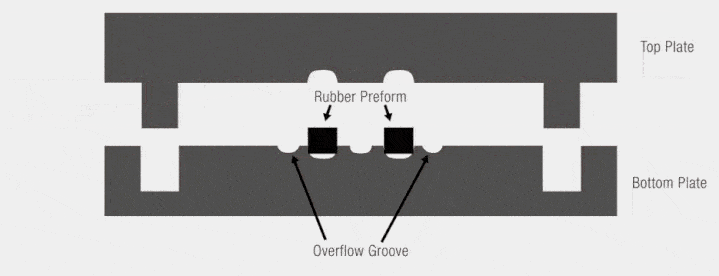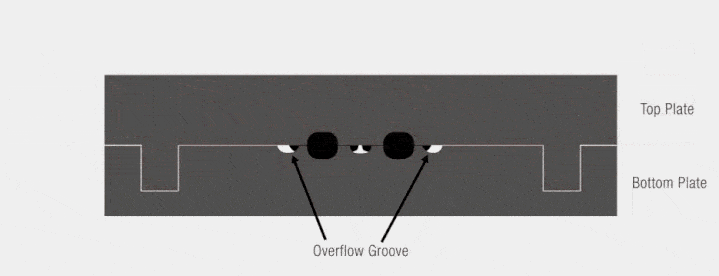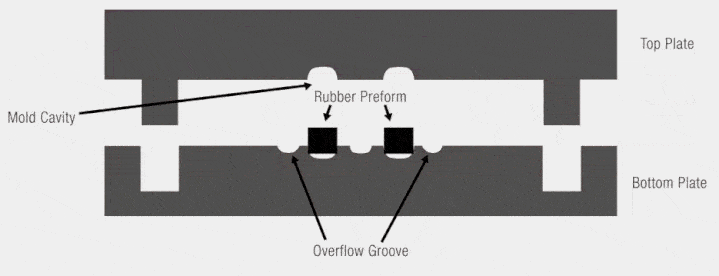
Common mold types include:
- Overflow molds
- Non-overflow molds
- Semi-overflow molds
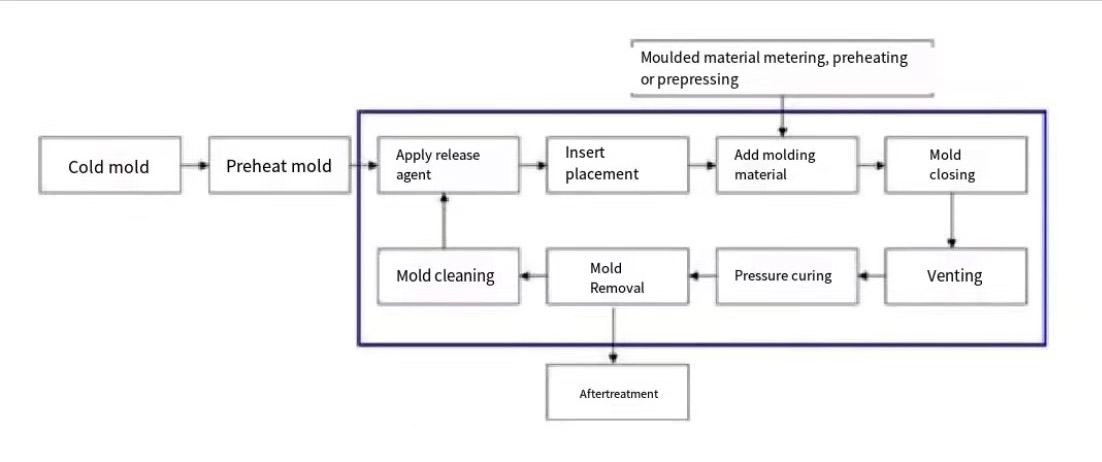
The Process Flow of Compression Molding
The typical process includes the following steps:
- Measuring: Accurate measurement is critical, using weight, volume, or counting methods.
- Pre-pressing: Reduces compression ratios and improves thermal transfer.
- Preheating: Increases curing speed and improves material flow.
- Insert Placement: Ensures correct positioning for components like conductive parts.
- Feeding: Accurate feeding is crucial for achieving desired product specifications.
- Closing Molds: Rapid initial closing followed by a slower approach to prevent damage.
- Ventilation: Essential for expelling gases and moisture during the process.
- Curing: Achieved through controlled pressure and temperature.
- Demolding: Typically occurs while the material is still warm, utilizing ejector rods.
- Post-processing: Involves additional treatments to ensure product quality.
Process Conditions and Control
The three critical factors in compression molding are pressure, temperature, and time. Balancing these factors optimizes product quality while minimizing production costs.
For more insights on thermosetting plastic compression molding, stay connected!