Discover the fundamentals of compression molding, key techniques, and essential tips for achieving high-quality results.
What is Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a manufacturing technique that shapes materials like SMC (Sheet Molding Compound), BMC (Bulk Molding Compound), and carbon fiber composites. It’s ideal for creating durable, high-performance components with complex geometries.
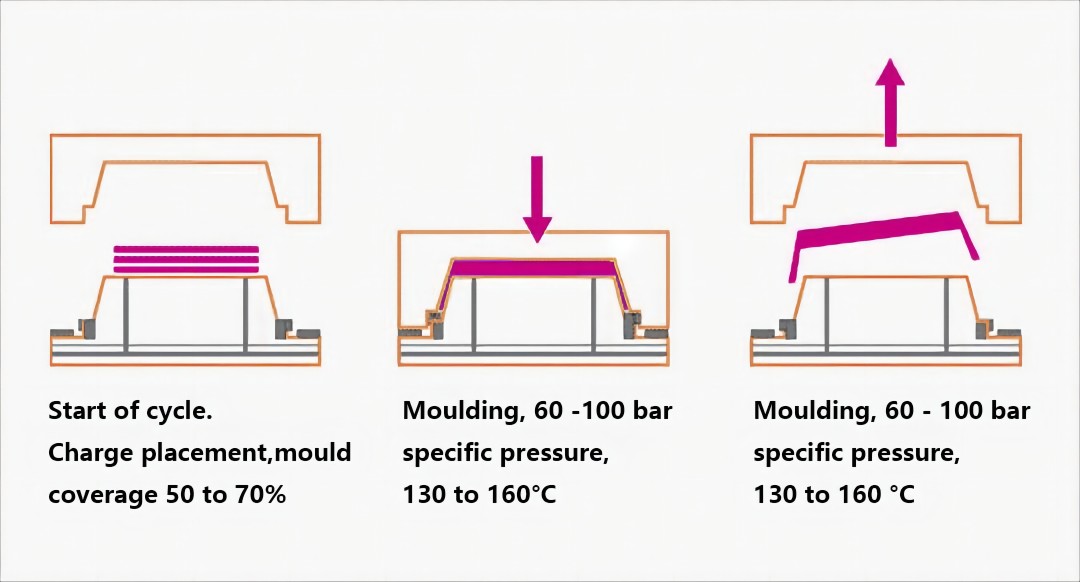
Key Steps in the Compression Molding Process
- Material Preparation: Preheat materials like SMC, BMC, or rubber for better flow and faster curing.
- Mold Loading: Proper material placement ensures uniform pressure and prevents defects.
- Compression and Curing: Heat and pressure are applied to shape and solidify the material.
- Cooling and Demolding: Controlled cooling reduces shrinkage and enhances dimensional stability.
- Trimming and Finishing: Flash removal, sanding, and coating improve the final product.
Common Materials for Compression Molding
| Material | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) | High strength, corrosion resistance | Automotive parts, electrical enclosures |
| BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) | Heat resistance, dimensional stability | Appliance parts, electrical components |
| Rubber | Flexible, durable under pressure | Seals, gaskets, vibration dampers |
| Carbon Fiber Composites | Lightweight yet extremely strong | Aerospace, automotive, performance parts |
Advantages of Compression Molding
- Cost-Effective: Ideal for large parts with minimal material waste.
- High Strength and Durability: Ensures robust products for demanding applications.
- Complex Geometries: Capable of producing intricate designs with precise details.
- Excellent Surface Finish: Provides smooth, high-quality surfaces that require minimal post-processing.

Challenges in Compression Molding
- Longer Cycle Times: Thermoset materials often require extended curing periods. Optimizing mold temperature reduces delays.
- Material Waste: Flash removal is necessary but can be minimized with precise mold design.
- Tooling Costs: While initial costs are higher, durable molds offset these expenses in high-volume production.
Expert Tips for Beginners
- Choose the Right Material: Select materials like SMC, BMC, or rubber based on your product’s durability and finish needs.
- Optimize Mold Design: Add proper venting to improve pressure distribution and reduce trapped air.
- Control Temperature and Pressure: Fine-tune these settings for consistent quality and reduced cycle times.
- Prioritize Mold Maintenance: Regular cleaning and lubrication enhance mold longevity.
Applications of Compression Molding
Compression molding is a versatile method used in various industries for producing durable, complex parts.
- Automotive: Engine covers, battery enclosures, and body panels.
- Electrical: Switchgear, insulators, and circuit breaker housings.
- Aerospace: Lightweight carbon fiber composite parts for enhanced performance.
- Consumer Goods: Kitchen appliances, furniture parts, and sporting equipment.
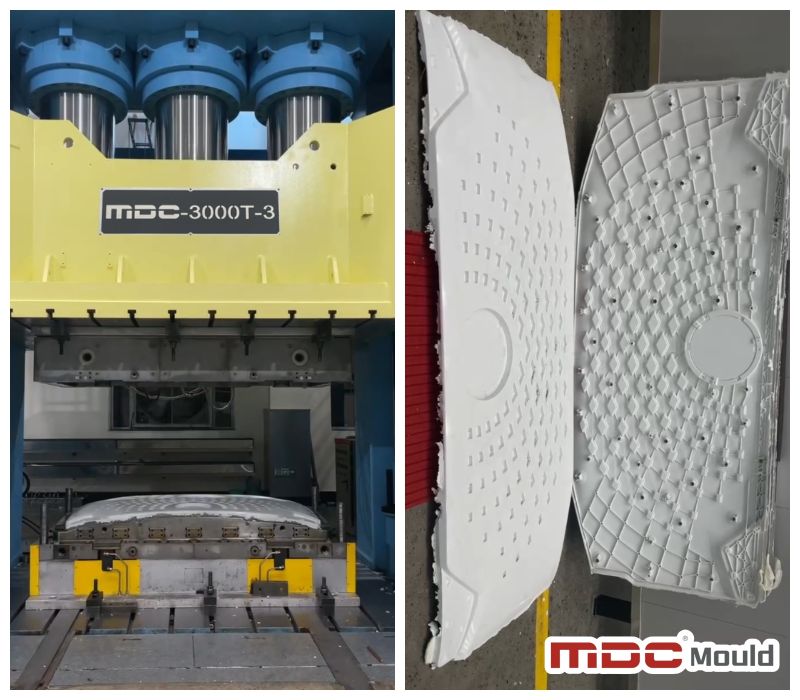

Conclusion
Compression molding is a powerful solution for creating durable, complex parts across multiple industries. For precise, high-performance molds, trust MDC Mould for professional solutions tailored to your needs. Mastering compression molding techniques and material selection ensures faster production cycles, improved quality, and reduced costs.