Discover the fundamentals of compression molding, key techniques, and essential tips for achieving high-quality results.
What is Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a manufacturing technique that shapes materials like SMC (Sheet Molding Compound), BMC (Bulk Molding Compound), and carbon fiber composites. It’s ideal for creating durable, high-performance components with complex geometries.
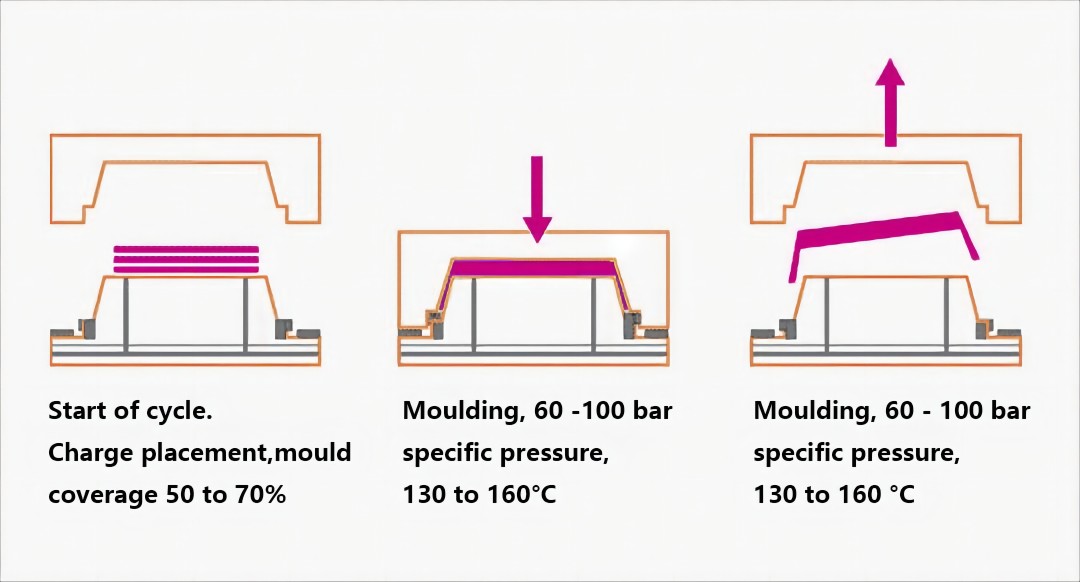
Key Steps in the Compression Molding Process
- Material Preparation: Preheat materials like SMC, BMC, or rubber for better flow and faster curing.
- Mold Loading: Proper material placement ensures uniform pressure and prevents defects.
- Compression and Curing: Heat and pressure are applied to shape and solidify the material.
- Cooling and Demolding: Controlled cooling reduces shrinkage and enhances dimensional stability.
- Trimming and Finishing: Flash removal, sanding, and coating improve the final product.
Common Materials for Compression Molding
| Material | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) | High strength, corrosion resistance | Automotive parts, electrical enclosures |
| BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) | Heat resistance, dimensional stability | Appliance parts, electrical components |
| Rubber | Flexible, durable under pressure | Seals, gaskets, vibration dampers |
| Carbon Fiber Composites | Lightweight yet extremely strong | Aerospace, automotive, performance parts |
Advantages of Compression Molding
- Cost-Effective: Ideal for large parts with minimal material waste.
- High Strength and Durability: Ensures robust products for demanding applications.
- Complex Geometries: Capable of producing intricate designs with precise details.
- Excellent Surface Finish: Provides smooth, high-quality surfaces that require minimal post-processing.

Challenges in Compression Molding
- Longer Cycle Times: Thermoset materials often require extended curing periods. Optimizing mold temperature reduces delays.
- Material Waste: Flash removal is necessary but can be minimized with precise mold design.
- Tooling Costs: While initial costs are higher, durable molds offset these expenses in high-volume production.
Expert Tips for Beginners
- Choose the Right Material: Select materials like SMC, BMC, or rubber based on your product’s durability and finish needs.
- Optimize Mold Design: Add proper venting to improve pressure distribution and reduce trapped air.
- Control Temperature and Pressure: Fine-tune these settings for consistent quality and reduced cycle times.
- Prioritize Mold Maintenance: Regular cleaning and lubrication enhance mold longevity.
Applications of Compression Molding
Compression molding is a versatile method used in various industries for producing durable, complex parts.
- Automotive: Engine covers, battery enclosures, and body panels.
- Electrical: Switchgear, insulators, and circuit breaker housings.
- Aerospace: Lightweight carbon fiber composite parts for enhanced performance.
- Consumer Goods: Kitchen appliances, furniture parts, and sporting equipment.

Conclusion
Compression molding is a powerful solution for creating durable, complex parts across multiple industries. For precise, high-performance molds, trust MDC Mould for professional solutions tailored to your needs. Mastering compression molding techniques and material selection ensures faster production cycles, improved quality, and reduced costs.
Wow! Thank you! I always needed to write on my blog something like that. Can I take a fragment of your post to my blog?