Understanding the Basics of Hot Press and Compression Molding
In the realm of material manufacturing and molding, hot press molding and compression molding are two widely utilized techniques. While they share similarities, their unique characteristics make them suitable for different applications. It’s important for manufacturers to understand these differences so they can choose the best process for their needs.
What is Hot Press Molding?
Hot press molding, often referred to as hot compression molding, involves applying heat and pressure simultaneously to shape and cure materials. This process is often used to make composite materials, like carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP), sheet molding compound (SMC), and bulk molding compound (BMC).
Key Features of Hot Press Molding
- Heat and Pressure Application: The mold is heated to a specified temperature, and pressure is applied to shape the material and start the curing process.
- Material Compatibility: It is particularly effective for thermosetting materials, which require heat to cross-link and harden.
- Precision and Strength: This method produces parts with excellent dimensional stability and high mechanical strength.
- Cycle Time: Hot press molding generally has longer cycle times due to the need for curing at elevated temperatures.
- Applications: It is used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics for parts such as EV battery enclosures, trunk boards, and engine splash shields.
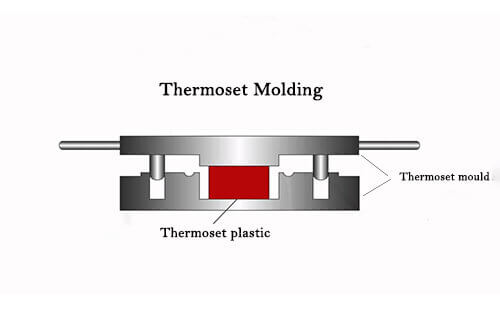
What is Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a widely used process where a material, typically a pre-measured amount of thermosetting polymer, is placed into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to shape the material as it cures.
Key Features of Compression Molding
- Simplicity: The process involves fewer steps compared to hot press molding, making it cost-effective for mass production.
- Material Use: Suitable for both thermosetting and thermoplastic materials.
- Cycle Time: Compression molding typically has shorter cycle times for thermoplastic materials, though thermosets may require extended curing.
- Versatility: It can produce a wide range of parts, from small precision components to large structural items.
- Applications: It is commonly used for producing SMC water tanks, GRP sectional tanks, and other fiberglass-reinforced plastic products.
Key Differences Between Hot Press and Compression Molding
| Feature | Hot Press Molding | Compression Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Application | Integral to the process; molds are heated | Optional; molds can be heated or room temperature |
| Pressure Application | Higher pressure required | Moderate pressure sufficient |
| Material Compatibility | Primarily thermosetting materials | Both thermosetting and thermoplastic materials |
| Precision | High dimensional accuracy | Moderate to high precision, depending on material |
| Cycle Time | Longer, due to curing requirements | Shorter, especially with thermoplastics |
| Applications | Advanced composites and structural components | Everyday plastic and composite parts |
Choosing the Right Process
When selecting between hot press molding and compression molding, manufacturers must consider the following factors:
- Material Type: Hot press molding is typically preferred when working with advanced composites like carbon fiber.
- Production Volume: Compression molding is more cost-effective for large-scale production runs.
- Part Complexity: Hot press molding is ideal for intricate shapes requiring high precision.
- Budget and Time Constraints: Compression molding offers quicker cycle times and lower costs for simpler parts.
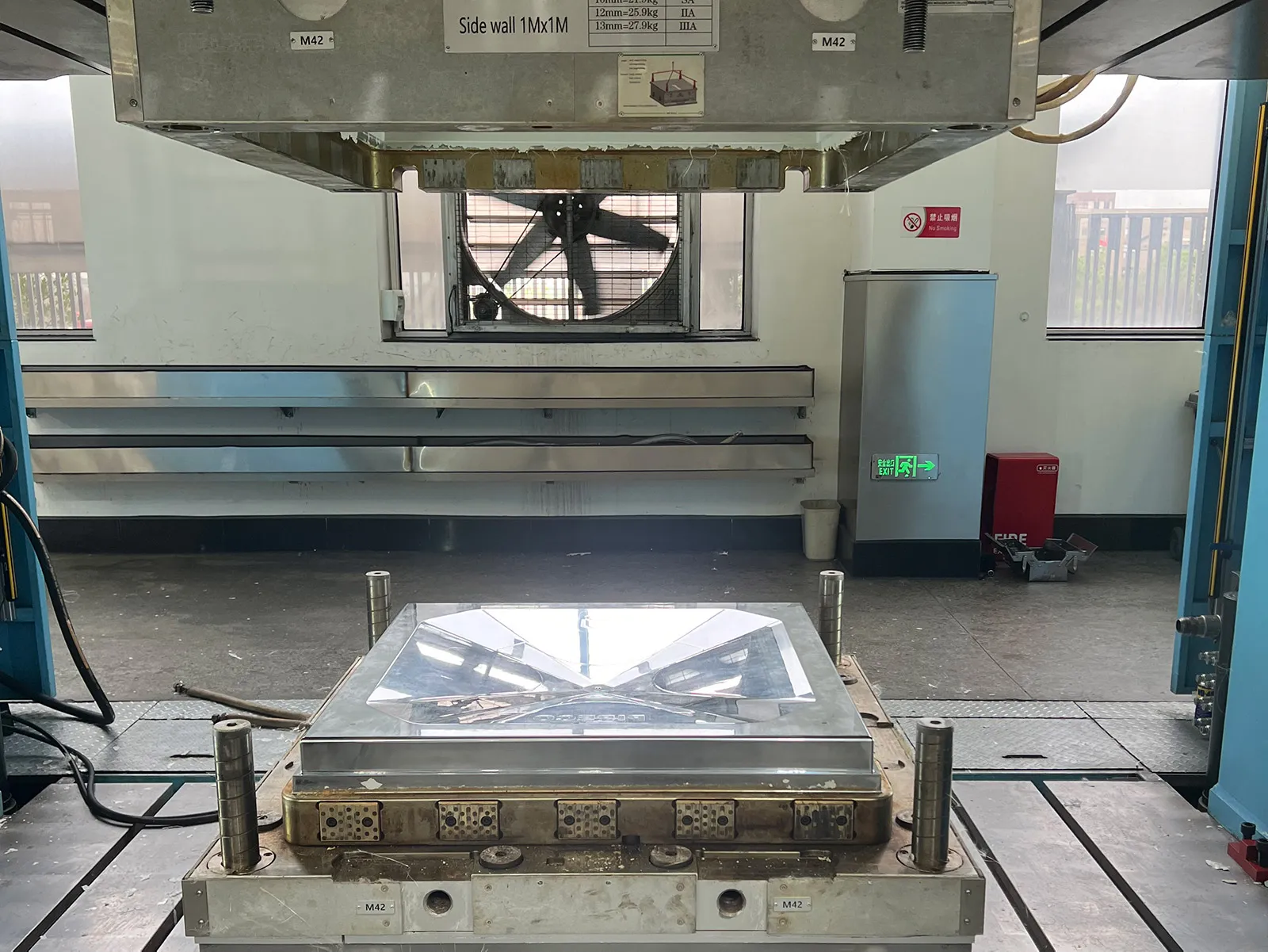

Applications Across Industries
Hot press and compression molding are used in many industries:
- Automotive: From SMC battery covers to engine splash shields, these methods produce high-performance components.
- Aerospace: Hot press molding is preferred for lightweight, high-strength parts.
- Construction: GRP water tanks and sectional tanks are commonly produced using compression molding.
- Consumer Goods: Compression molding is often used to make everyday plastic items like handles and housings because it is cost-efficient.
Conclusion
Hot press molding and compression molding are both very important in modern manufacturing. Hot press molding is great at making strong, precise parts. Compression molding is good for making a lot of different things, and it’s cheap. By understanding the differences between these methods and knowing when to use them, manufacturers can make better products.