The release of the Auman Galaxy truck by Foton Daimler marks a groundbreaking moment in the commercial vehicle industry, blending sleek design with optimal performance. Integral to this innovation is the advanced SMC mold technology provided by Zhejiang MDC Mould Co., Ltd., responsible for manufacturing crucial structural components of the truck.
SMC Molds: Turning Vision into Reality
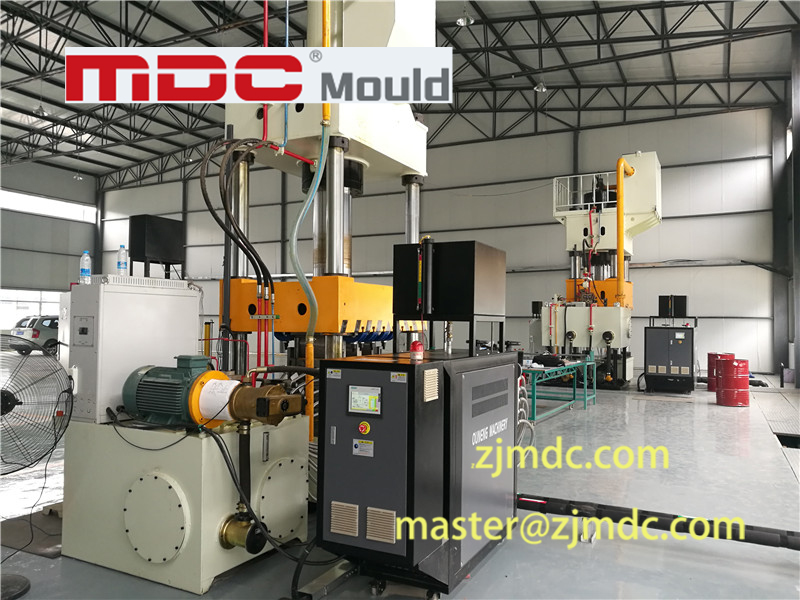
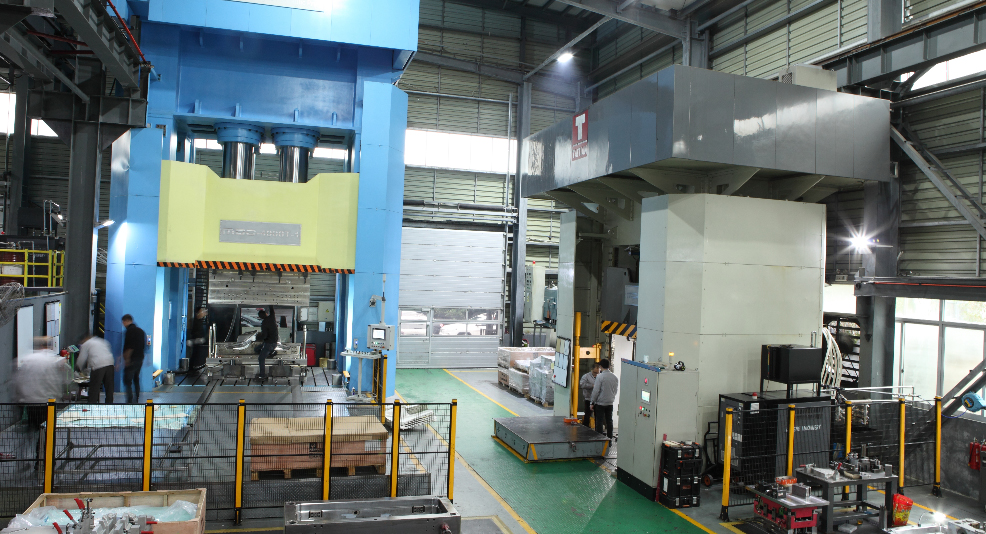
MDC Mould worked tirelessly to bring this project to life. From the concept stage to serial production, the company created state-of-the-art SMC molds including molds for the SMC roof spoiler, SMC front face panel, and SMC air deflector. In just 12 weeks, MDC Mould transformed these components from prototypes to high-quality serial tools.
This achievement not only reflects MDC’s technical expertise but also highlights their commitment to meeting demanding deadlines without compromising quality.

Understanding SMC Materials in Automotive Manufacturing
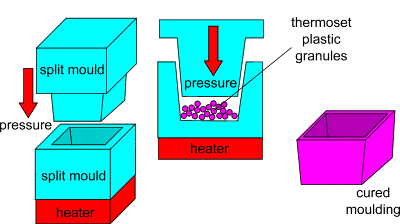
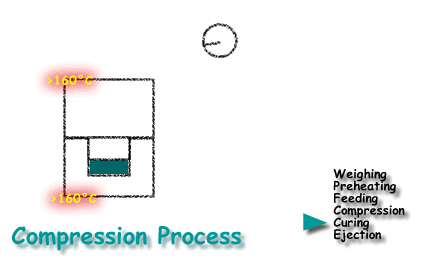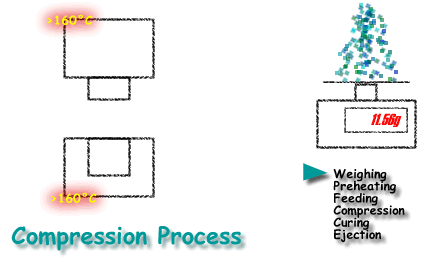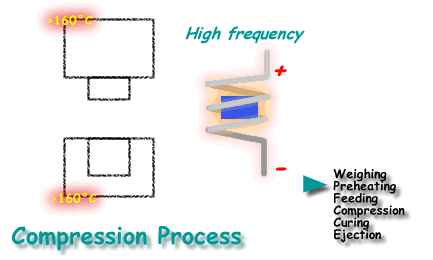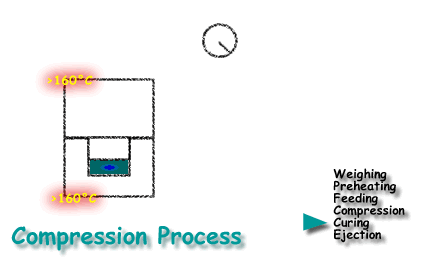
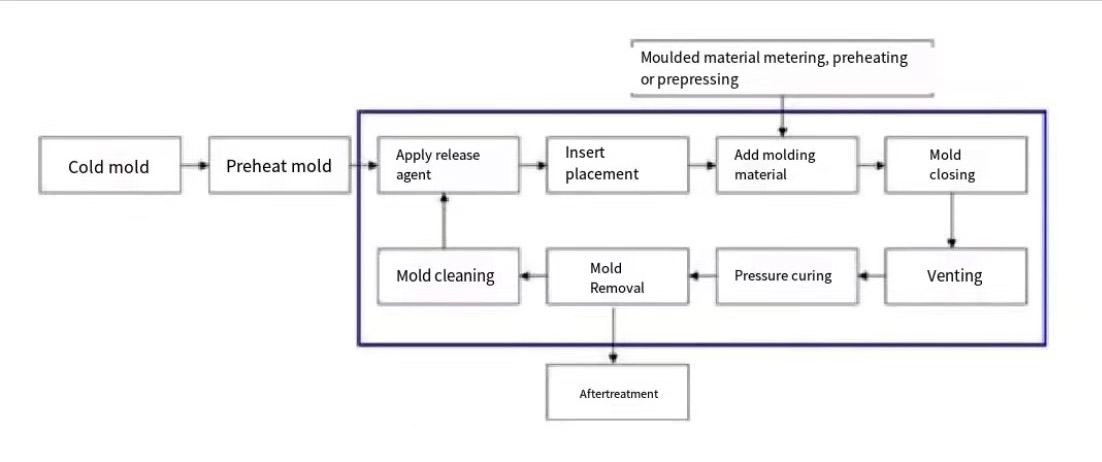
Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) is a composite material made from thermosetting resins, glass fibers, and other additives, and is widely used in automotive manufacturing. Its combination of strength, durability, and lightweight properties makes it ideal for vehicle parts that require high performance while reducing weight.
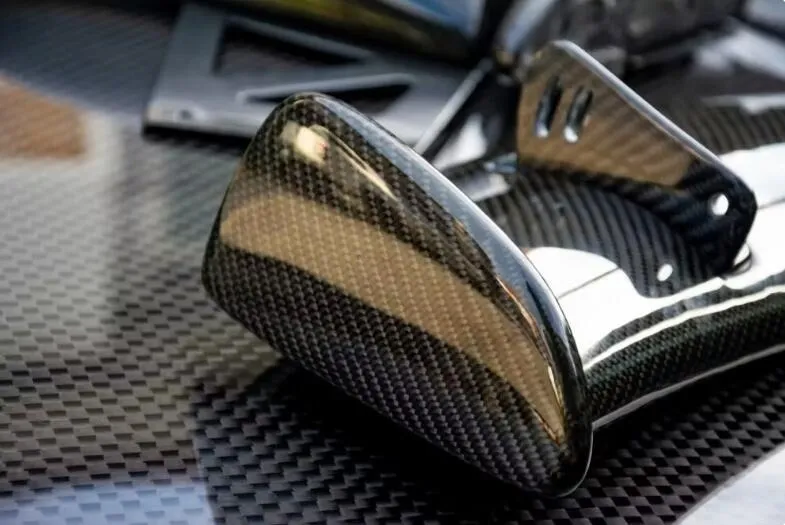
For the Auman Galaxy truck, MDC Mould’s SMC molds were essential in creating parts such as the roof spoiler, front face panel, and air deflector, improving aerodynamics and enhancing the vehicle’s overall efficiency.
Advantages of SMC in Automotive Components
SMC offers several key advantages in the automotive sector:
- Lightweight: Reduces the overall weight of vehicles, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, which is especially important for electric vehicles like the Auman Galaxy.
- High Strength: Despite being lightweight, SMC components offer excellent structural integrity, capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions and mechanical stress.
- Corrosion Resistance: SMC parts are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for exterior automotive components exposed to the elements.
- Cost-Effective: SMC’s efficiency in the molding process reduces manufacturing costs while maintaining high product quality.
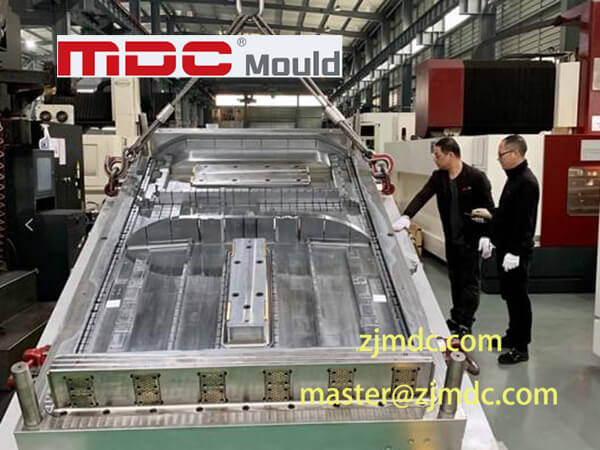

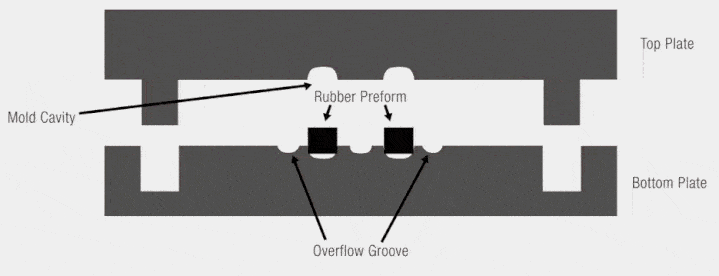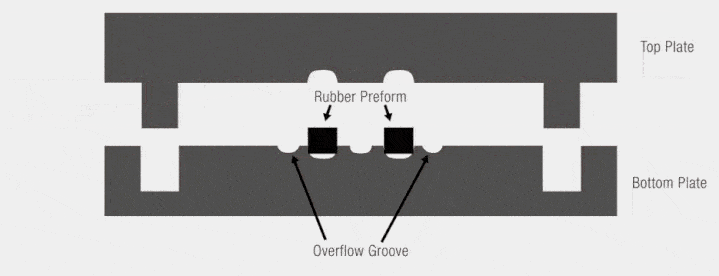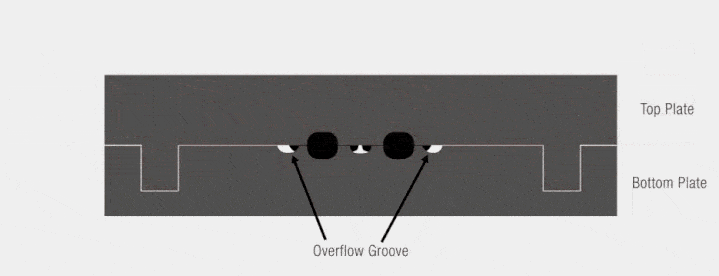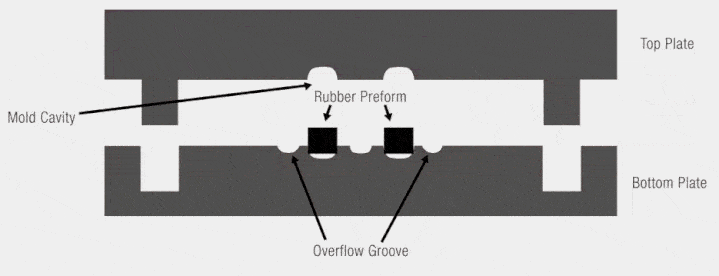
Detailed Overview of SMC Molds for the Auman Galaxy Truck
1. SMC Roof Spoiler Mold
The SMC roof spoiler mold provided by MDC Mould was designed with precision, ensuring optimal aerodynamics and a perfect fit. The roof spoiler not only enhances the truck’s sleek appearance but also contributes to improved fuel efficiency by reducing drag.
2. SMC Front Face Panel Mold
The SMC front face panel mold adds a distinctive touch to the truck’s exterior. This component offers both style and function, giving the vehicle a strong front-end appearance while maintaining durability and impact resistance.
3. SMC Air Deflector Mold
The SMC air deflector mold is another critical component manufactured by MDC Mould. It helps in directing airflow smoothly around the truck, reducing air resistance and noise, thereby contributing to a more fuel-efficient and quieter ride.
Rapid Tooling for Urgent Projects
From prototype to serial tool production, MDC Mould completed the development of these molds in just 12 weeks. Their rapid tooling capabilities make them an ideal partner for projects with urgent lead times. This speed doesn’t come at the expense of quality; MDC Mould employs cutting-edge technology to ensure every mold meets strict industry standards.
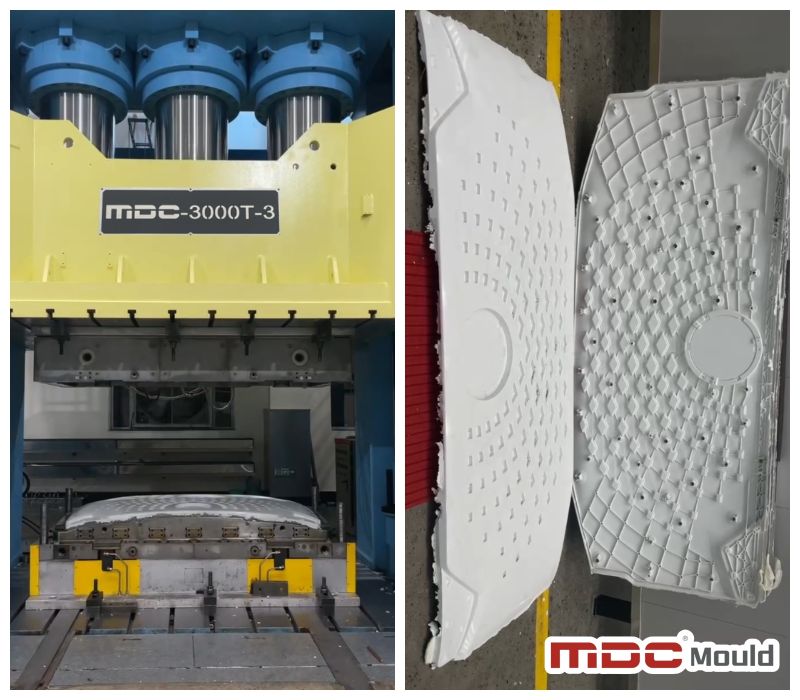

MDC Mould’s Commitment to Quality and Innovation
With years of experience in the automotive mold industry, MDC Mould is a trusted partner for companies looking for high-quality, reliable molds. Their expertise spans across various sectors, including electric vehicles, making them a leader in the development of SMC molds for the next generation of trucks and cars.
MDC Mould’s team is always ready to take on new challenges, providing tailored solutions for every project. Whether you need SMC molds, compression molds, or other composite mold solutions, MDC Mould is equipped to meet your needs with precision and efficiency.
Partner with MDC Mould for Your Next Project
If your project has a tight timeline or specific technical requirements, reach out to MDC Mould for innovative solutions. Their team is committed to delivering high-quality molds on time, ensuring that your production stays on track.