Thermoforming is a widely used process in the manufacturing industry, especially when producing plastic components. The process involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes pliable and then shaping it against a mold. In thermoforming, the mold type plays a crucial role in determining the final product’s quality, accuracy, and surface finish. Two primary types of molds are used in this process: the positive mold (also known as the male mold) and the negative mold (also known as the female mold). Understanding the differences between these molds is essential for anyone involved in thermoforming or related fields such as composite mold and compression mold manufacturing.
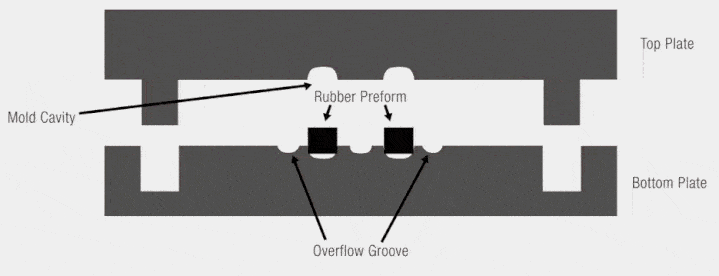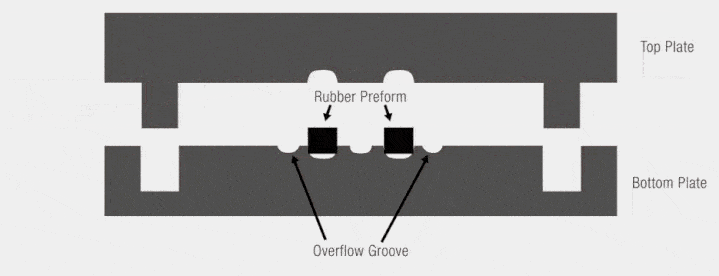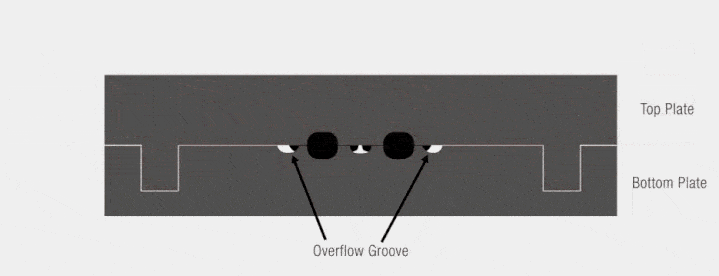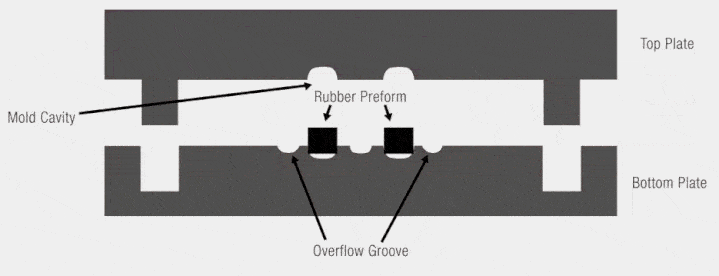
Positive Mold (Male Mold)
A positive mold, or male mold, is a type of mold where the material is formed over the exterior surface. The mold itself represents the shape that will be transferred to the inner surface of the final product. This means that the material is stretched over the mold, with the exterior of the material taking the shape of the mold’s exterior.
Key Characteristics of Positive Molds:
- Surface Finish: The outer surface of the product directly contacts the mold, providing a high-quality finish on the internal surface. This is ideal for applications where the inner surface’s texture or appearance is critical.
- Material Stretching: The plastic sheet is stretched over the mold, which can lead to thinning in areas, especially around corners and edges.
- Application: Positive molds are often used when the internal dimensions are more important than external ones. For example, in applications involving thermoforming molds for containers or trays, where the inside must be smooth and accurate.
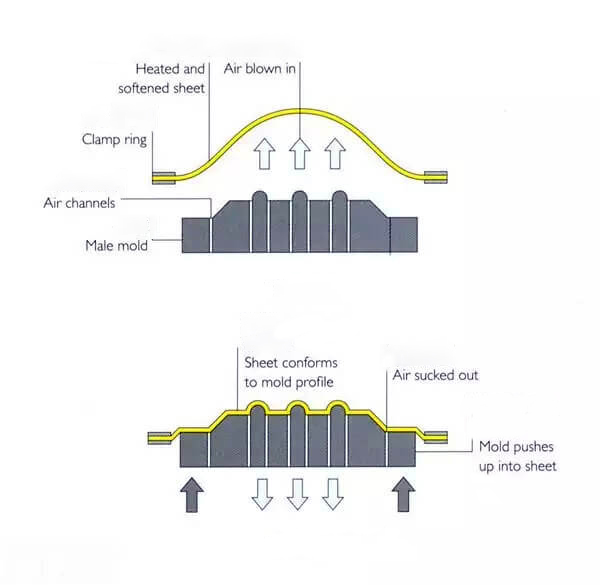
Negative Mold (Female Mold)
A negative mold, or female mold, is the inverse of a positive mold. In this case, the material is drawn into the mold, allowing the outer surface of the material to match the mold’s interior. The external surface of the final product mirrors the internal surface of the negative mold.
Key Characteristics of Negative Molds:
- Surface Finish: The outer surface of the product takes the finish of the mold’s interior. This results in a high-quality surface on the exterior of the final product.
- Material Thickness: Since the material is drawn into the mold, it tends to maintain a more consistent thickness, which is beneficial for applications requiring uniform strength.
- Application: Negative molds are used when the external appearance and dimensions of the product are critical. This is common in composite molds and compression molds, where external aesthetics are important.
Comparing Positive and Negative Molds
Both positive and negative molds have their advantages and limitations, and the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the application.
- Surface Quality: Positive molds offer a superior finish on the internal surface, whereas negative molds provide a better finish on the external surface.
- Material Distribution: Negative molds tend to produce parts with more uniform wall thickness, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent material strength.
- Design Flexibility: Positive molds may lead to thinning in the material at sharp corners, which could be a limitation in certain designs.
Applications in Composite Molding
The principles of positive and negative molds extend beyond traditional thermoforming into the realm of composite molding. In composite molds used for producing high-performance parts, such as carbon fiber molds, the choice between positive and negative molds can impact the final part’s structural integrity and surface quality.
- SMC Mold and BMC Mold: Both Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) and Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) processes utilize molds that must withstand high pressures and temperatures. Here, the choice of a positive or negative mold can affect the part’s surface texture and material flow.
- Carbon Fiber Mold: In carbon fiber mold manufacturing, the mold type influences the fiber alignment and resin distribution, crucial for achieving the desired strength-to-weight ratio.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between positive and negative molds in thermoforming is essential for optimizing the manufacturing process. Positive molds provide high-quality internal surfaces but can lead to material thinning, while negative molds offer uniform material distribution and superior external finishes. Whether in traditional thermoforming or advanced composite molding applications, choosing the right mold type is crucial for achieving the desired product characteristics. As technologies evolve, the principles behind positive and negative molds continue to shape industries ranging from packaging to aerospace, highlighting their ongoing importance in manufacturing.