Over the past few decades, composite materials have become important in traffic engineering, automotive, aerospace technology, electrical engineering and other industries. Composites based on Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) and Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) technologies allow the creation of small and medium-sized parts with the highest mechanical properties and heat resistance requirements.
Thermoset materials such as SMC, BMC, etc have excellent physical properties when getting compression molding. Structural parts molded from BMC or SMC can be replaced for metal products at the condition of weight reduction without lowering strength. Excellent heat resistance, compression strength, and dimensional stability are all advantages of compression molding materials.
Difference Between SMC and BMC Materials
Before the introduction begins, there are a few more proper nouns you need to know:
- Polyester resin: an adhesive that provides three-dimensional crosslinking during processing, connects individual components, and plays an important role in achieving desired thermomechanical properties;
- Mineral fillers: ensuring the transport of glass fibers during the flow of the material, can significantly reduce its cost and, in the case of aluminum hydroxide, significantly improve the refractoriness of the material;
- Glass fiber: provides the mechanical strength of the product;
- Catalyst: Provides initiation of three-dimensional cross-linking chemical reactions. The correct choice of catalyst is the most important condition for obtaining high-quality parts without underpressure, cracks and voids.
SMC material
SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) – Sheet material containing resins, fillers, reinforcing fibers. SMC is a material that can be pressed and processed at a high temperature of 120-160 SMC °C. The SMC is protected by a polymer film on both sides. Thickening agent, inorganic filler, initiator, additive, and pigment were added to the unsaturated polyester resin to make a mixture of resin, impregnated with short-cut fiber or felt piece, covered with PE film on both sides, after thickening, a thin sheet molded plastics were prepared. Unlike woven glass materials, SMC is not reinforced with bonded glass fibers. Because the glass fiber length is significantly longer than that of BMC, SMC has lower flow properties but higher strength properties. By using a chemical-resistant resin, a pressed material with high weather resistance can be obtained.
Typical SMC structure:
- Fiberglass (15-50mm) – 27%;
- Filler (talc) – 40%;
- Resins (polyester, vinylester) – 28%;
- Other additives – 5%.
Usually fibers in SMC products have two orientations. SMC also has the following varieties:
- SMC LP is a thin material that can get products with high surface quality;
- SMC LS – low shrinkage material;
- HSSMC is a high strength material.
Depending on the specific product, different types of SMC can be used, each with different characteristics. The common denominator is minimal technical shrinkage and high impact strength. The significant advantages of SMC products compared to steel are high corrosion resistance and low specific gravity. SMC is processed into large-sized body parts by direct compression. During the pressing process, the pre-cut material is placed into the mold. The clamping time is 2-3 minutes, and the heating temperature is about 150 ℃.
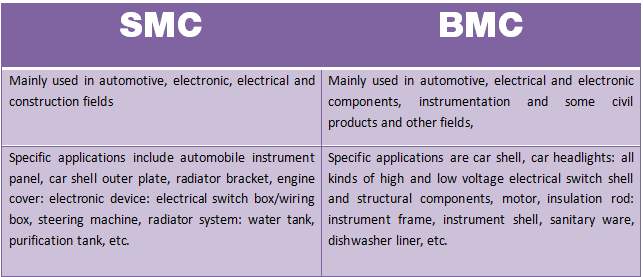
The main application areas of SMC are: automotive industry, traffic engineering, lighting engineering, electrical network. The most notable achievement is the use of oil pans and valve covers made of SMC by car companies in production truck models. The following is a list of auto parts that can be manufactured with compression molds.
- Automotive exterior parts: bumper linings, mudguards, wheel covers, spoilers and rear doors.
- Automotive interior parts: instrument panel, door panel, glove box, car seat and various protection panels.
- Structural and functional components: fuel tank, coolant tank, air filter cover, fan blades, intake pipe and cylinder head.
In addition to auto parts, SMC molding is also used to produce bathroom accessories, water tank accessories, motorcycle accessories, fitness equipment parts and meter housings.
BMC material
BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) – A special paste-like material containing resin BMC, fillers, and reinforcing fibers. It mixes a variety of inert fillers, fiber-reinforced materials, catalysts, stabilizers and pigments in thermosetting plastics to form a gluey “putty like” composite material for pressing or injection molding. The glass fibers in BMC are shorter than those in SMC, so the BMC material flows even better than SMC, and can be made into a better finish or more complex materials. BMC features light weight, electrical insulation, fire resistance, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, weather resistance, low shrinkage, stable dimensional control, good fluidity, and a variety of special properties combined into one, making bulk molding compound (BMC) the most ideal of materials to manufacture smaller but more complex and precise products used in various industries.
Typical BMC structure:
- Fiberglass (5-20mm) – 20%;
- Filler (talc) – 45%;
- Resins (polyester, vinylester) – 30%;
- Other additives – 5%.
BMC is a material that can be processed by pressing or injection. During pressing, metal is used to heat the substrate. Pressures from 30 to 100 atmospheres. The heating temperature is 100-160°C. The mold closing time is 2-3 minutes, during which heating occurs and polymerization is initiated. Injection molding uses a screw injection molding machine to feed material into a closed mold cavity.
BMC technology has also been widely used in the production of complex-shaped parts, such as pump casings, electrical components, etc.
Although there are differences between the two forms of material, both are suitable options for compression molding. In both cases, MDC mould offers SMC and BMC mould options that accompany MDC mould’s commitment to excellence.
SMC VS BMC
| In general, when the mechanical properties of the products, including tensile strength, bending strength and impact strength, etc. are higher, the surface area of the products is larger, and the lightweight of the products is higher, SMC will be selected. | In general, the requirements for economic cost control are too high, and the mechanical strength requirements are lower than SMC requirements; When the electrical properties and flame retardant properties of the products are higher; When the surface area of the product itself is small, people usually choose BMC. |
| SMC is light weight and high strength | Size stability of BMC |
| SMC integration degree is high, design freedom | BMC has good water and solvent resistance |
| SMC has strong corrosion resistance | High heat resistance of BMC |
| SMC excellent heat resistance and coating | Aging resistance of BMC |
| SMC pressing process is simple | The electrical performance of BMC is outstanding |
MDC mould has been designing and manufacturing moulds for Sheet Moulding Compound (SMC) and Bulk Moulding Compound (BMC) materials since the 1990s. MDC Mould is one of well-known mold makers in china. With the most advanced production equipment and technology, it enables us to manufacture the best quality molds. MDC has a long history in the glass fiber compression molding industry. We are committed to the design, development and production of stampers, as well as provide technical support to customers worldwide, Our aim is to become the best supplier of stable, high-performance SMC mould and BMC mould.