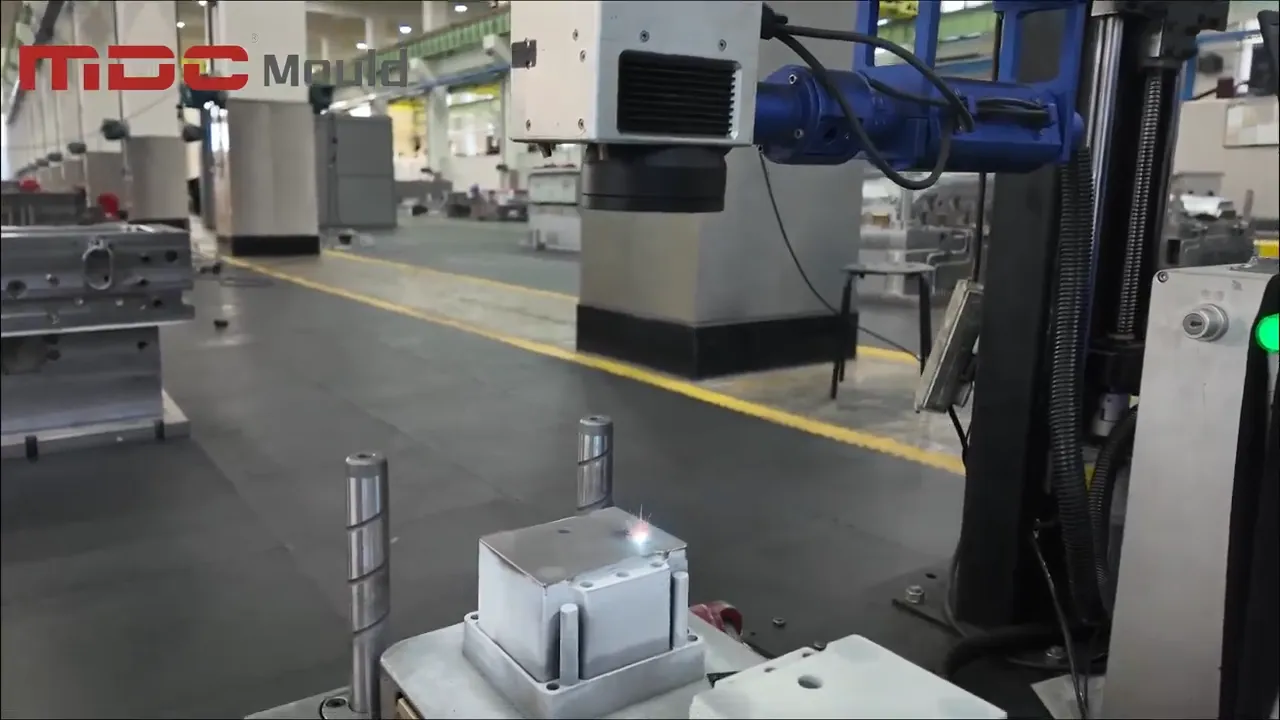
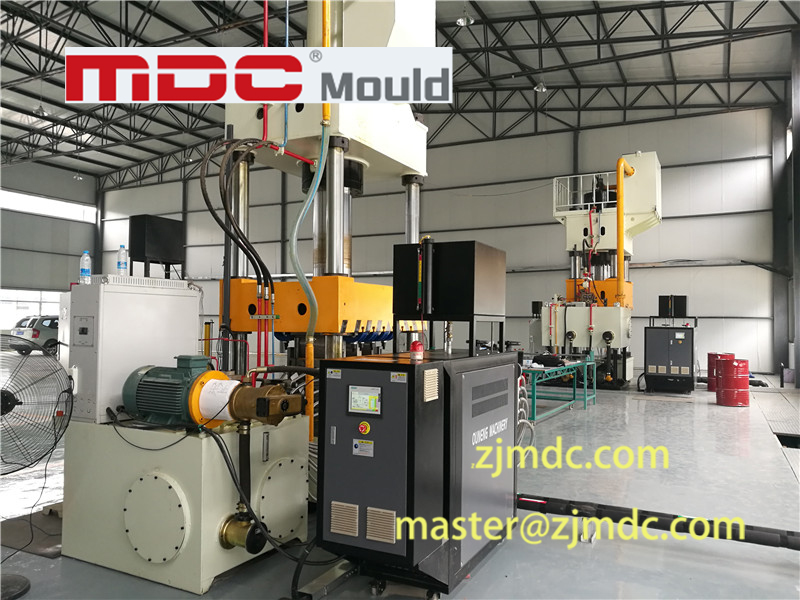
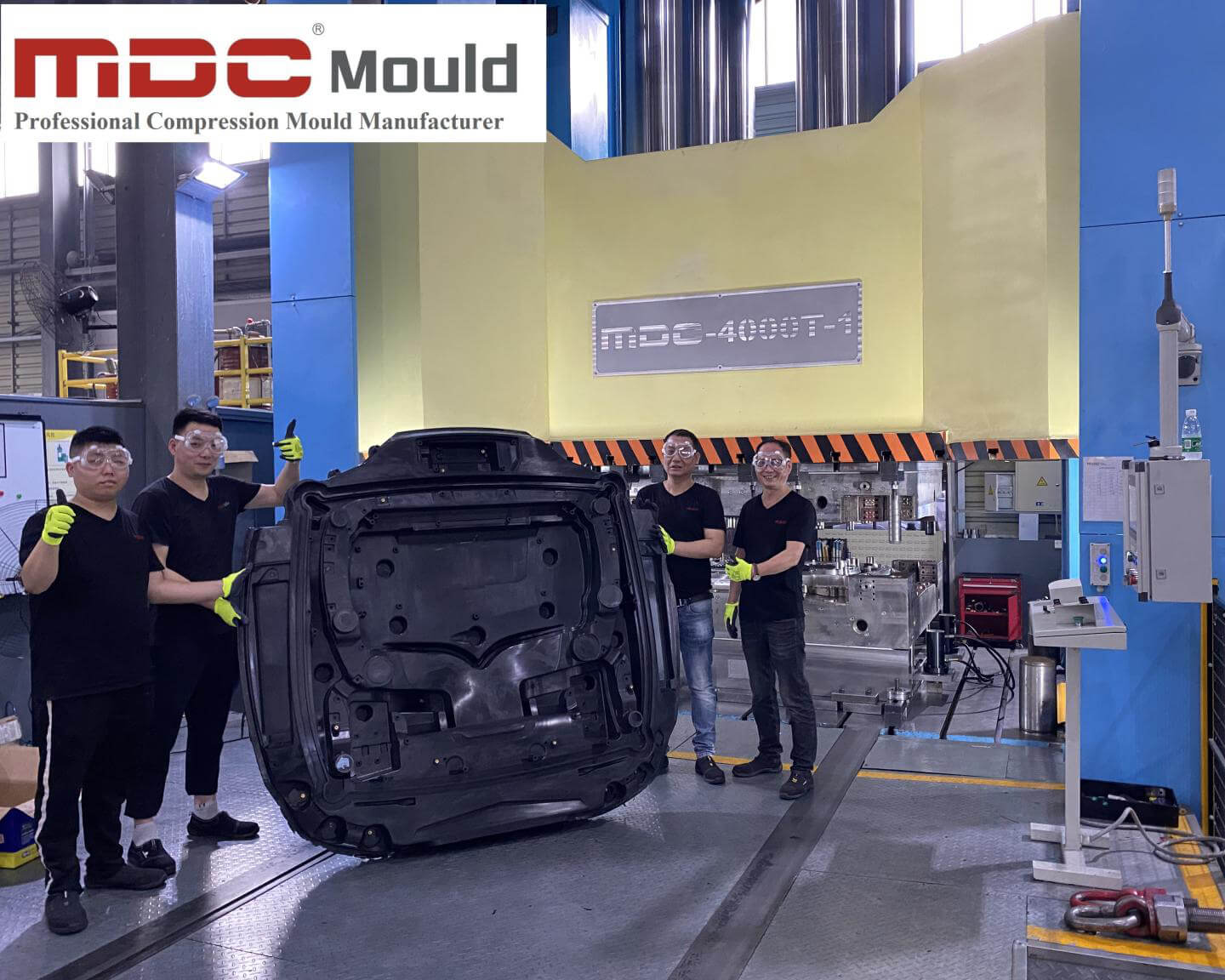
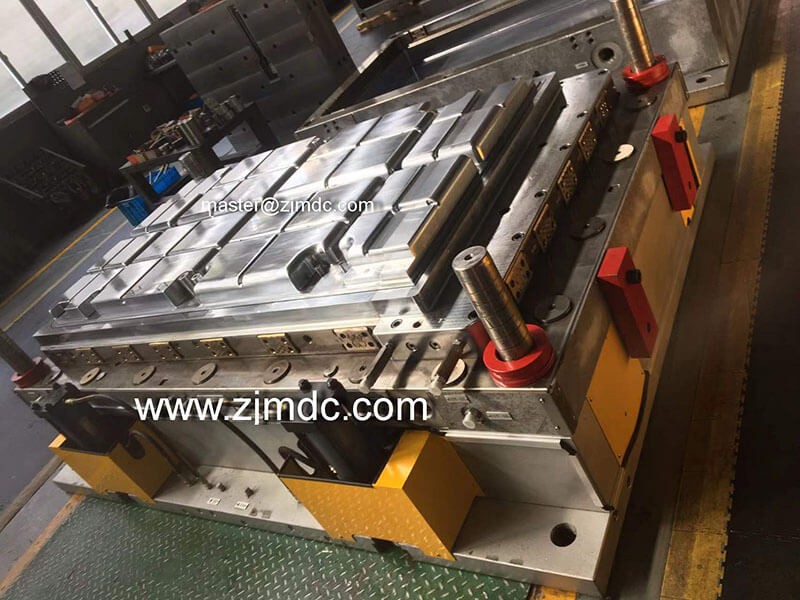
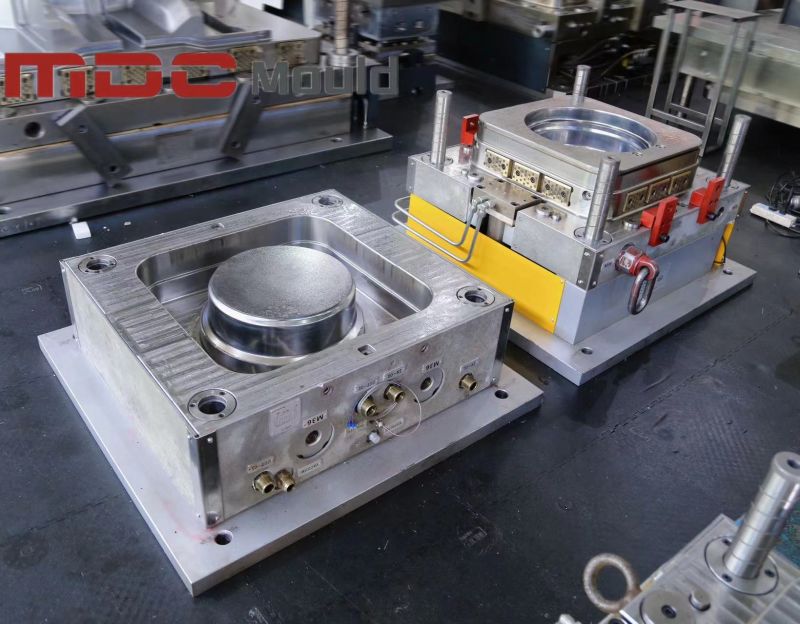
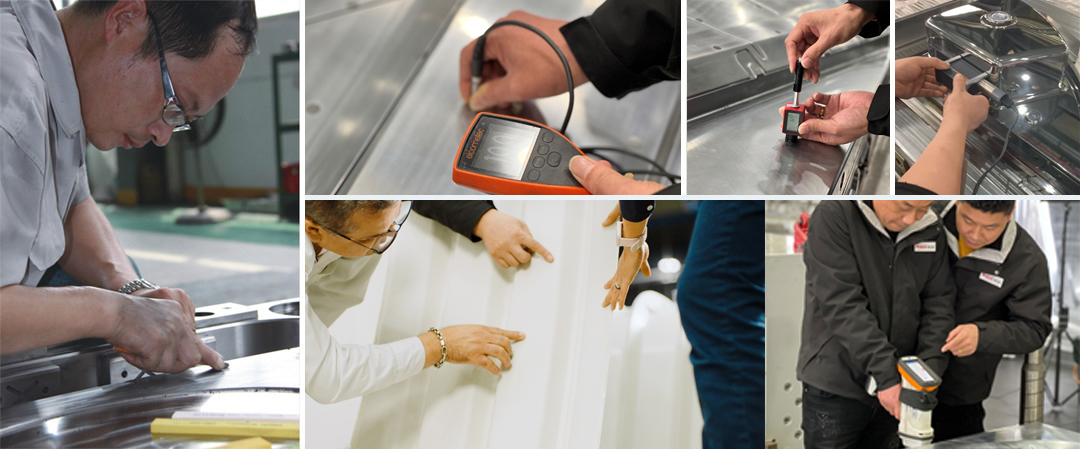
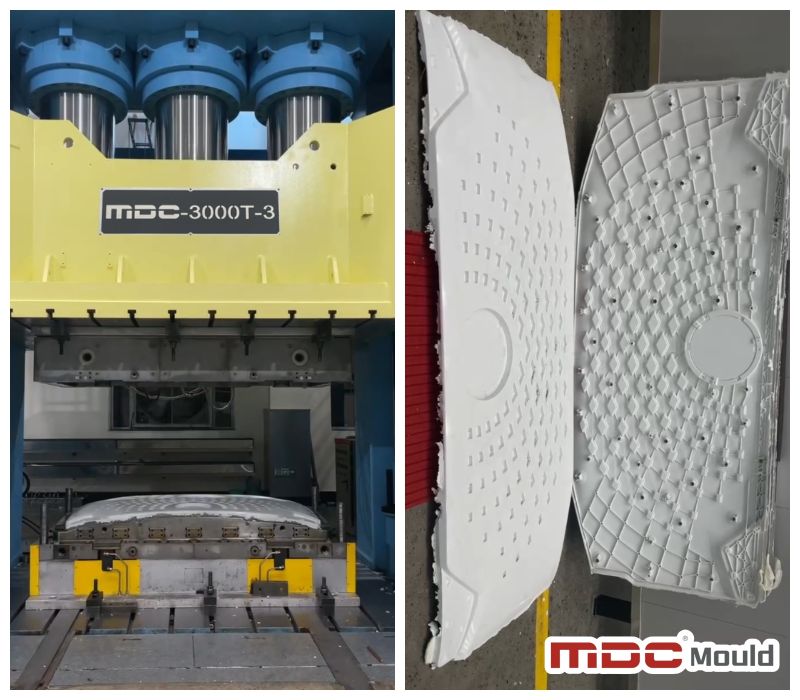
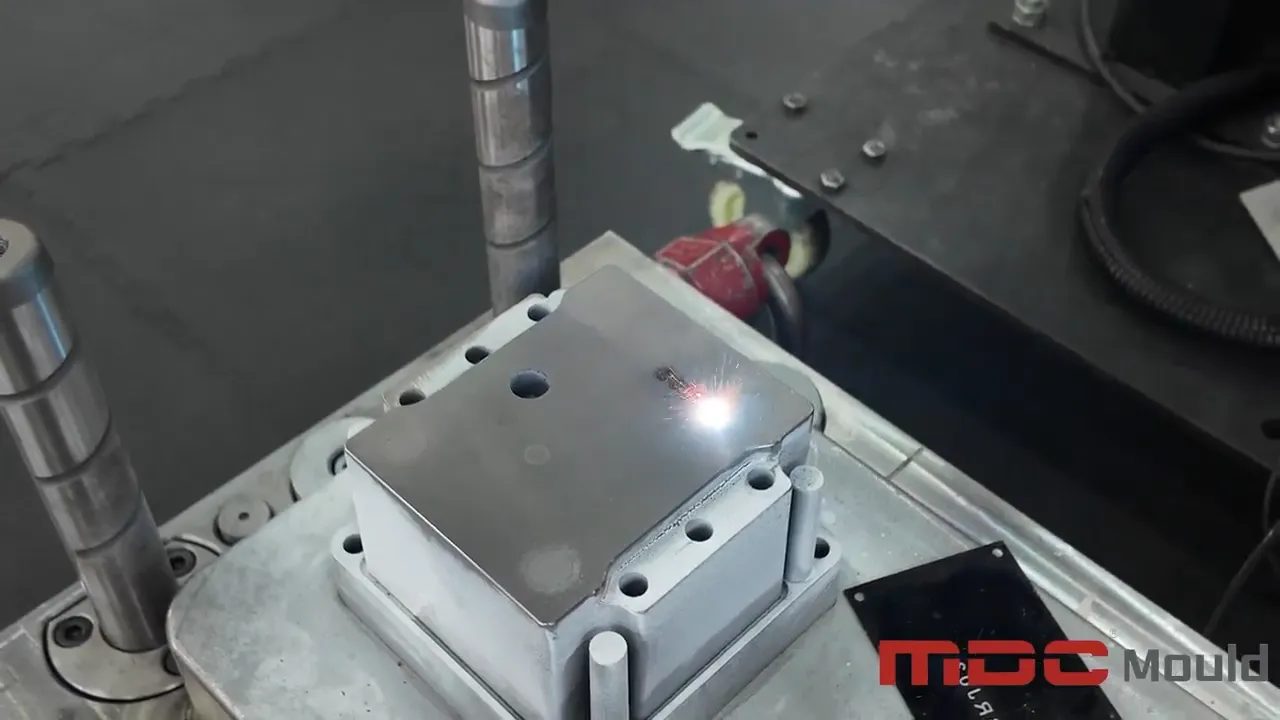
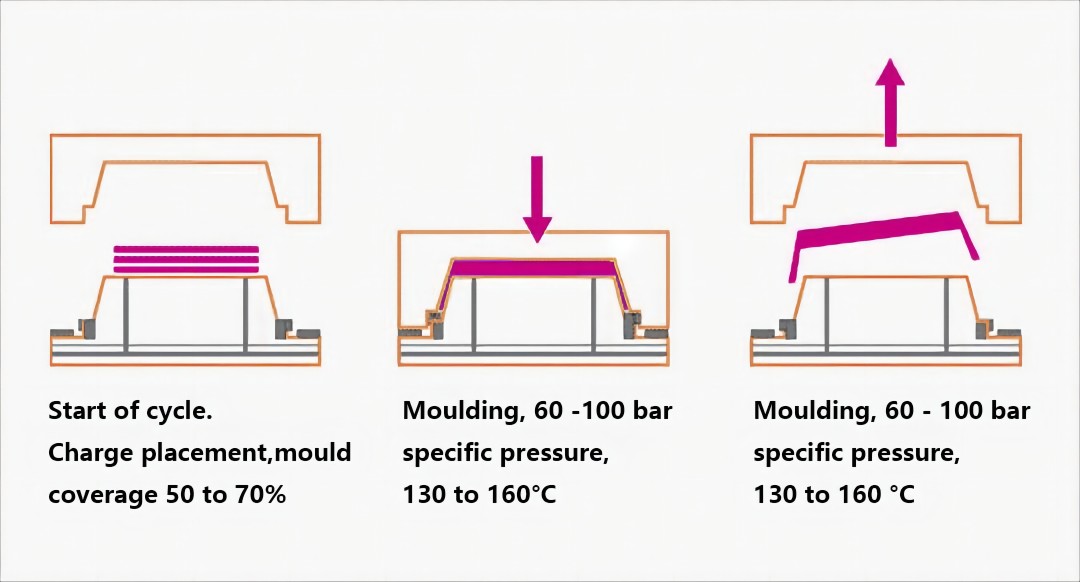
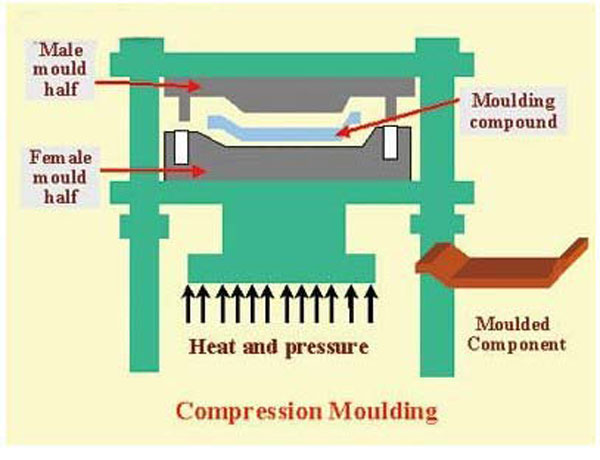
In the world of high-performance mold manufacturing, deep hole drilling is more than just a machining step—it’s a precision process that defines the long-term success of a mold. At MDC Mould, we apply high-accuracy CNC deep hole drilling machines to prepare the internal structure of each mold before it enters fine machining. This ensures not only precision, but long-term mold performance and product reliability.
What is Deep Hole Drilling?
Deep hole drilling refers to the process of machining holes with a high depth-to-diameter ratio, typically for mold components that require internal fluid flow paths. Our CNC drilling equipment delivers tight tolerances, excellent straightness, and smooth internal surfaces critical for high-performance mold operations.
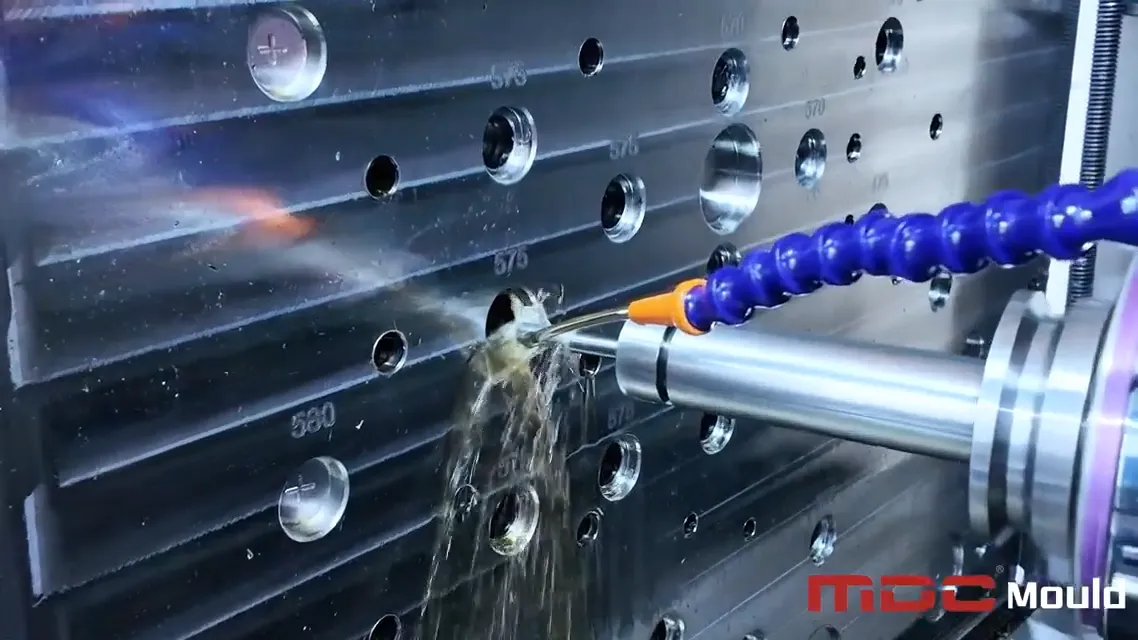

Applications of Deep Hole Drilling in Composite Molds
Our drilling processes play a vital role in optimizing mold function and performance across multiple areas:
1. Cooling Water Channels
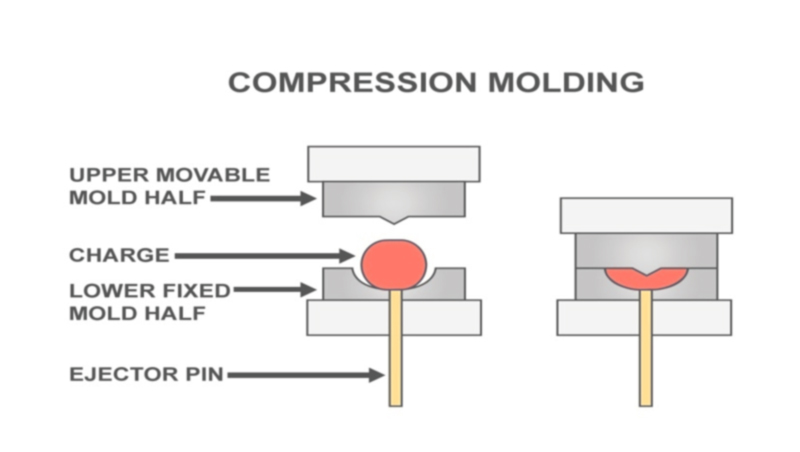
Precision-drilled cooling channels allow for efficient heat transfer and shorter cycle times in compression molding and injection molding operations.
2. Ejector Pin Guide Paths
Accurate ejector pin paths ensure smooth demolding, reducing wear and avoiding misalignment during part ejection.
3. Vacuum and Venting Lines
In SMC/BMC composite molds, vacuum lines and vents are essential to eliminate trapped air and improve part quality by minimizing surface defects.
4. Oil Heating Channels
Thermoset molds often require oil-based heating. Our high-precision drilling ensures leak-free, thermally optimized channels to maintain stable mold temperatures during production.
Why Accuracy in Drilling Matters
The quality of a mold’s internal channels has a direct effect on its long-term functionality and energy efficiency. Key benefits of precision deep hole drilling include:
- Uniform mold temperature distribution
- Shorter cycle times due to optimized thermal control
- Increased mold lifespan with reduced stress
- Fewer defects and improved part surface quality
- Improved energy efficiency and productivity
Every channel drilled is more than a hole—it’s a foundation for consistent mold performance and production stability.
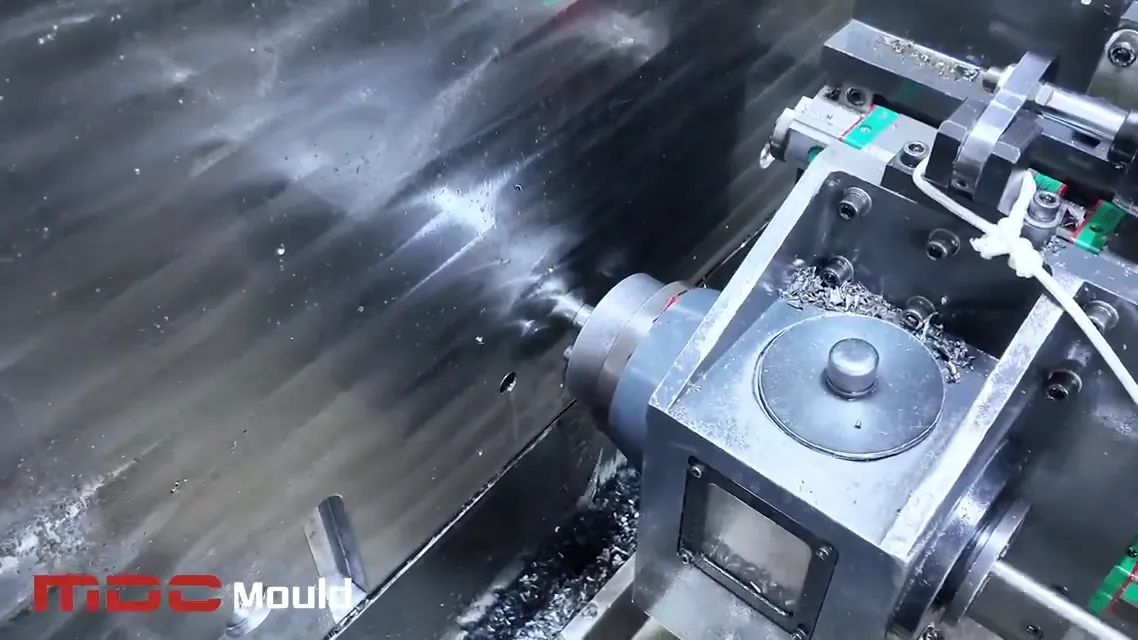

Advanced Equipment for High-Performance Tooling
Our facility is equipped with multi-axis CNC deep hole drilling machines capable of producing high-precision holes even in complex mold geometries. We support drilling in:
- SMC molds and BMC molds
- Carbon fiber composite molds
- Automotive component molds (e.g., trunk boards, battery covers)
- FRP water tank and square GRP tank molds
- EV enclosures and engine splash shield molds
CNC Deep Hole Drilling Capabilities
At MDC Mould, our deep hole drilling process incorporates:
- Precision tolerances down to ±0.05mm
- Drilling depths up to 1500mm with excellent straightness
- Surface finishes meeting Ra ≤ 1.6μm
- Compatibility with hardened steels, aluminum, copper, and thermoset tooling plates
Our integrated CAD/CAM system ensures each drilled hole aligns perfectly with 3D mold designs, reducing downstream machining errors and improving manufacturing efficiency.
MDC Mould: Your Trusted Partner in Composite Tooling
At MDC Mould, we offer end-to-end mold making services—from concept and CAD design to tooling and delivery. Our expertise in deep hole drilling supports the long-term success of your composite tooling projects.
We are dedicated to solving technical challenges in thermoset compression molding and continuously invest in precision engineering and tooling innovation to meet the evolving needs of global industries.